Newtons Laws EX 34
(a) The block is at rest. Therefore, the net force on the block is zero. We know that the block is subject to a horizontal force of 30 N to the right. Consequently, the force of friction points to the left (see the diagram - note that we made the assumption that the 30 N force is exerted by a boy pulling the box to the right). Since the two forces are "balanced", we conclude that also has magnitude 30 N. Note that in this case we did not use the formula for the maximum force of static friction but used, instead, Newton's Second Law to find it. Remember that the force of static friction is less than or equal to the product of the coefficient of friction and the magnitude of the normal force.
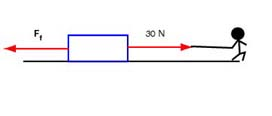
(b) If the block is moving to the left then the force of friction is just that of kinetic friction. Friction opposes the direction in which the block slides, which is to the left, as shown in this diagram:
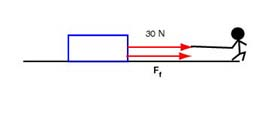
The normal force in this case is equal to the weight which is 50 N. (Can you justify this in words? If not, come and ask.) Since the coefficient of kinetic friction is equal to 0.5, the force of kinetic friction equal to 25 N. The net force exerted on the object (m = 5 kg) is equal to 55 N and the acceleration is given by . Note that in this case the object is moving to the left and slowing down (because velocity and acceleration point in opposite directions).
If the block is moving to the right then the force of kinetic friction points to left. The kinetic friction opposes the slide of the block, which we see is to the right:
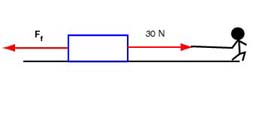
The (magnitude of the) normal force is still equal to that of the weight, 50 N, and the force of kinetic friction is equal to 25 N. The net force exerted on the object (m = 5 kg) is equal to 5 N, and is directed to the right. The acceleration is equal to . Note that in this case the object is moving to the right and acceleration is also pointing to the right. Therefore the block is speeding up.


