Newton's Laws
Newton's Three Laws of Motion
Newton's First Law of Motion
"A body continues in a state of rest, or of uniform motion in a straight line, unless acted upon by an external force."
In other words, an object remains at rest or moves at constant velocity when
Newton’s first law is based on the principle of inertia. The tendency of a body to resist a change in its state of motion is called inertia.
Newton's Second Law of Motion
"An object of mass moves with an acceleration that is defined by ."
Thus, the acceleration of a body is directly proportional to the net force acting on the body, and is inversely proportional to its mass.
Newton's Third Law of Motion
"For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction."
In other words, if body applies a force on body , then body applies an equal and opposite force on body .
Convention for the subscripts: If a force is exerted by an object A on an object B then we write this force as follows:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KeNye0nTqmM
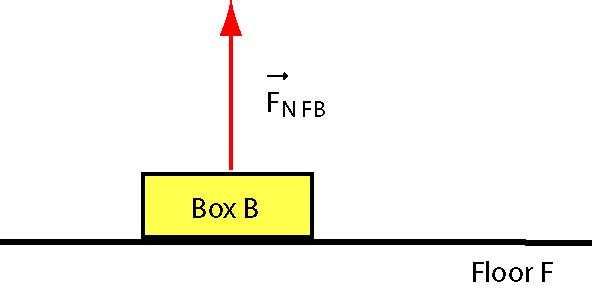
- Focus on notation: The first subscript indicates the particle which exerts the force; the second subscript indicates the particle on which the force is exerted. For example, the normal force exerted by the floor () on a box () in the diagram below should be labelled
- Action/reaction pairs: The two forces and form an action-reaction pair if and only if the two forces are of the same type (a normal force and a gravitational force cannot be an action-reaction pair) and if and only if we can write that
For example: which is a gravitational force exerted by the Earth on the man and which is a gravitational force exerted by the man on the Earth are the action-reaction pair.
On the other hand, which is a gravitational force exerted by the Earth on the man and which is the normal force exerted by the surface of the Earth on the man are not the action-reaction pair.
- Application of these concepts to find the acceleration of systems — problem solving strategy:
- Define a system of particles that you will study — each particle should be dealt with separately;
- List external forces acting on each particle use the notation which indicates the agent and then draw arrows to represent each external force in the diagram;
- Draw a free body diagram for each particle:
- Select and draw an "appropriate" coordinate system for each particle so that
- The x-axis is parallel to the direction in which a particle may possibly move or the direction of possible acceleration;
- The orientation of the x-axis for each particle in the system must be in the same sense;
- The positive y-axis is oriented +90º from the positive x-axis.
- Transfer the arrows representing forces into this system (each arrow has the tail at the origin).
- Determine the angle each arrow makes with the positive x-axis.
- Select and draw an "appropriate" coordinate system for each particle so that
- Write all forces in terms of their x- and y-components: for a given force of magnitude and direction , and
- Write equations for each particle or
- Write equations for each particle
- Identify all the action-reaction pairs.
- Solve the system of equations.
- An overview of the forces acting on a body in a mechanical system:
- Gravitational force:
- Special case of a gravitational force (close to the surface of Earth):
- Contact forces: Tension, Normal force and Friction.
- Force of a spring: restoring force
- Tension is caused by a restoring force acting between particles of thin long objects: rope, rod, beam, string, etc.
- The direction of the tension is always parallel to the thin object.
- Normal force is caused by a restoring force acting between particles of surfaces; it is always perpendicular to the surface.
- Friction occurs when two surfaces are in contact. It is due to an interaction between surface particles of one object and surface particles of the second object.